However, many states have not yet modernized their policy or process, making it significantly challenging for transgender people to access identification that matches their gender identity and protects their safety. This map examines the variation in state policies regarding both the process of changing one's gender marker, as well as the gender marker options available in a given state. This map's categories were developed in conversation with the National Center for Transgender Equality (NCTE) and based on their driver's license process grading system, available here.
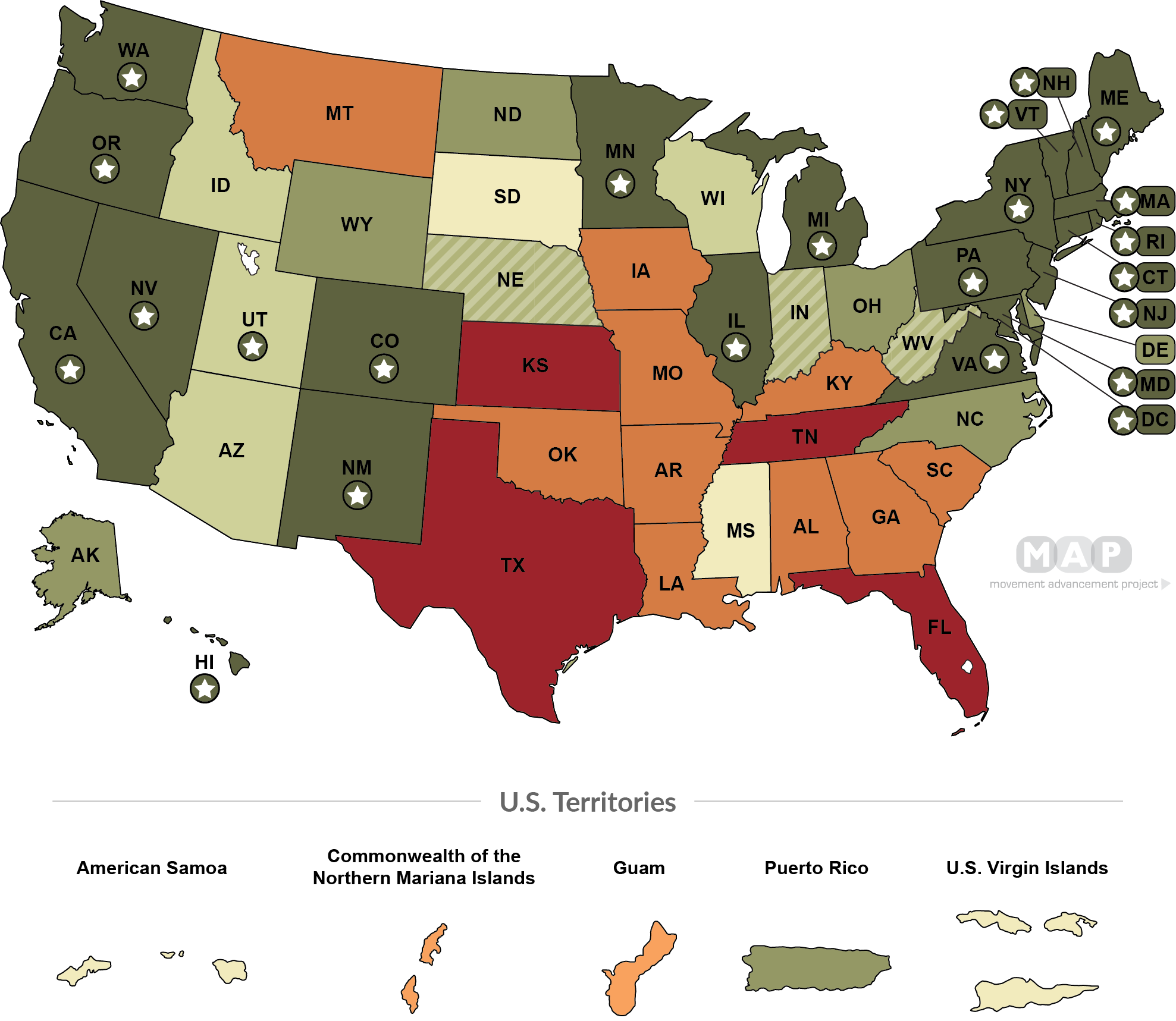
- State allows residents to mark M, F, or X on their driver's license (22 states + D.C.)
-
State uses easy to understand form and does not require provider certification (21 states + D.C.)
-
State uses easy to understand form and requires provider certification (accepted from wide range of professionals) (6 states, 1 territory)
-
State uses easy to understand form and requires provider certification (accepted from limited range of professionals) (3 states)
-
State has no form. No court order or proof of surgery required, but burdensome process requirements and/or provider certification required from limited range of professionals (4 states)
-
State has unclear, unknown or unwritten policy regarding gender marker changes (2 states, 2 territories)
-
State requires proof of surgery, court order, or amended birth certificate (10 states, 2 territories)
-
State does not allow for updating the gender marker on driver's license (4 states)
- In Arkansas, a March 2024 proposed "emergency" rule immediately ended the state's 14+ year policy of allowing "X" options on driver's licenses and significantly altered the process for changing the gender marker (to either M or F). The new process only allows for a driver's license update if the person has also amended their birth certificate. However, Arkansas makes it extremely difficult to do so, requiring both a court order and "surgical procedure"--and the state also explicitly allows health insurers to refuse to cover transgender-related medical care.
- In Florida, a January 2024 policy change banned gender marker changes on driver's licenses. While the agency's memo mentions potential criminal and/or civil penalties for transgender people having an ID that matches their gender identity, it is beyond the authority of the agency to unilaterally declare or reinterpret the state's criminal and/or civil statutes. MAP's resources will continue to be updated as events unfold in the state.
- In Kansas, a July 2023 court order is preventing people from changing the gender on their driver's license at all, pending an ongoing lawsuit about a recently enacted state law defining sex in ways that enable discrimination against transgender people. This map will be updated as events unfold in the state.
- See also MAP’s 2022 report The ID Divide: How Barriers to ID Impact Different Communities and Affect Everyone, detailing the ways that barriers to obtaining an accurate ID significantly impact people’s ability to move through their daily lives and how these obstacles harm specific communities, as well as our related Fact Sheet: Identity Documents & Transgender and Nonbinary Communities (2022).
Recommended citation:
Movement Advancement Project. "Equality Maps: Identity Document Laws and Policies." https://www.mapresearch.org/equality-maps/identity_document_laws. Accessed [day of access].
Percent of Transgender Population Covered by Laws
*Note: These percentages reflect estimates of the transgender population (ages 18+) living in the 50 states and the District of Columbia. Estimates of transgender people in the U.S. territories are not available, and so cannot be reflected here. Population estimates are from The Williams Institute.
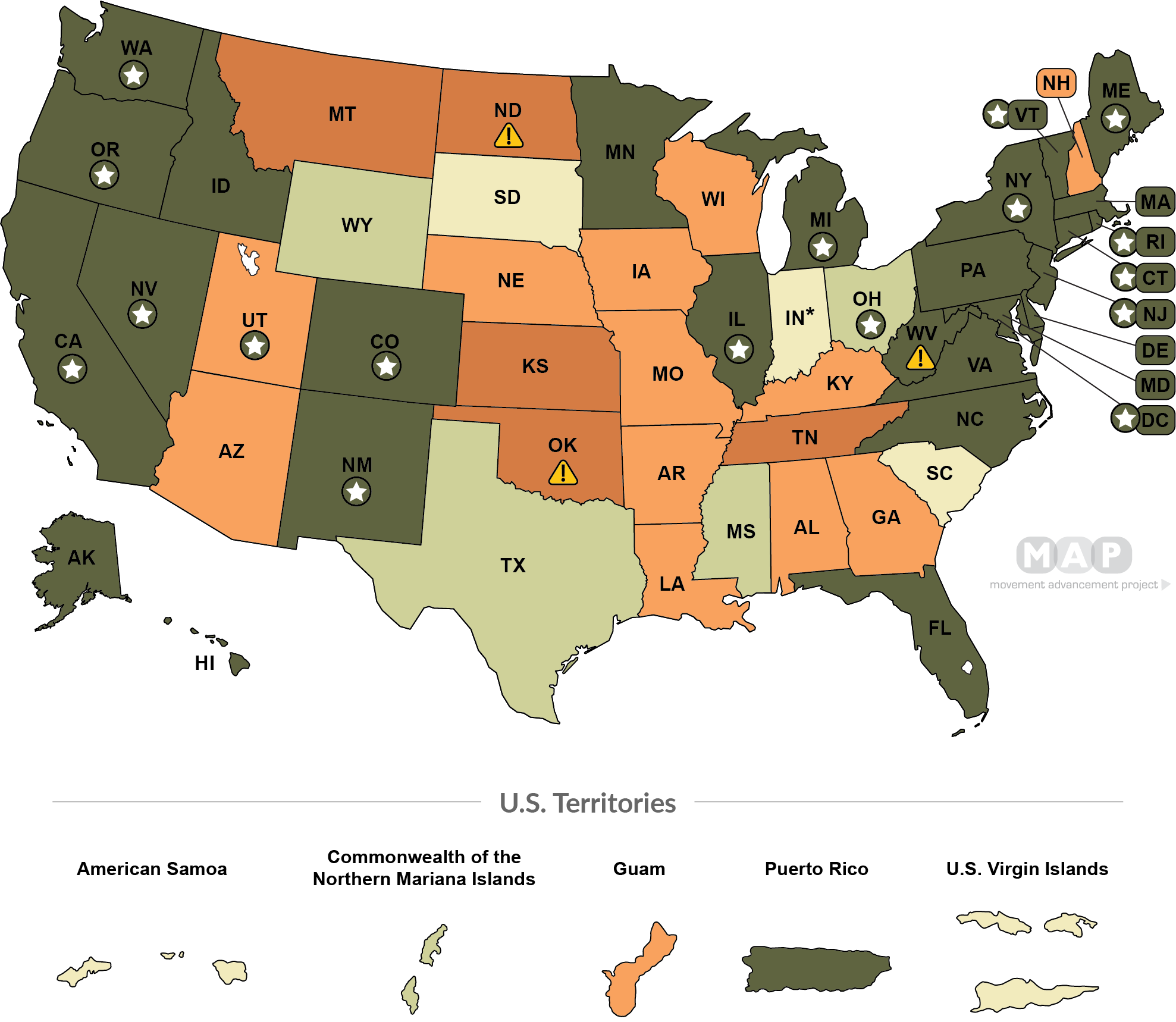
- State allows residents to mark M, F, or X on their birth certificates (16 states + D.C.)
-
State updates birth certificates using an administrative process and does not require provider documentation (14 states)
-
State updates birth certificates using an administrative process and requires provider documentation of "appropriate treatment" (11 states , 1 territory + D.C.)
-
State has unclear process and/or unclear medical requirements left to the discretion of individual judges (see citations for more information) (6 states, 3 territories)
-
State updates birth certificates using an administrative process but requires proof of surgery (3 states)
-
State updates birth certificates but requires both a court order and proof of surgery (8 states, 1 territory)
-
State does not allow for amending the gender marker on the birth certificate (8 states)
- State bans the use of an X option on birth certificates (3 states)
--Iowa's 2025 law does not go into effect until July 1, 2025. Until then, the state's law should allow individuals to update their birth certificate using an administrative process and proof of "appropriate treatment," though this may be subject to state officials' discretion given the impending law. See the Citations & More Information for more detail.
--North Dakota's 2023 law bans all gender marker changes on birth certificates with a narrow exception for individuals who have had genital surgery. This is a stricter, more explicit surgical requirement than in many other states. See the "Citations & More Information" for further detail.
- See also MAP’s 2022 report The ID Divide: How Barriers to ID Impact Different Communities and Affect Everyone, detailing the ways that barriers to obtaining an accurate ID significantly impact people’s ability to move through their daily lives and how these obstacles harm specific communities, as well as our related Fact Sheet: Identity Documents & Transgender and Nonbinary Communities (2022).
Recommended citation:
Movement Advancement Project. [Year of access]. "Equality Maps: Identity Document Laws and Policies." https://www.mapresearch.org/equality-maps/identity_document_laws. Accessed [day of access].
Percent of Transgender Population Covered by Laws
*Note: These percentages reflect estimates of the transgender population (ages 18+) living in the 50 states and the District of Columbia. Estimates of transgender people in the U.S. territories are not available, and so cannot be reflected here. Population estimates are from The Williams Institute.
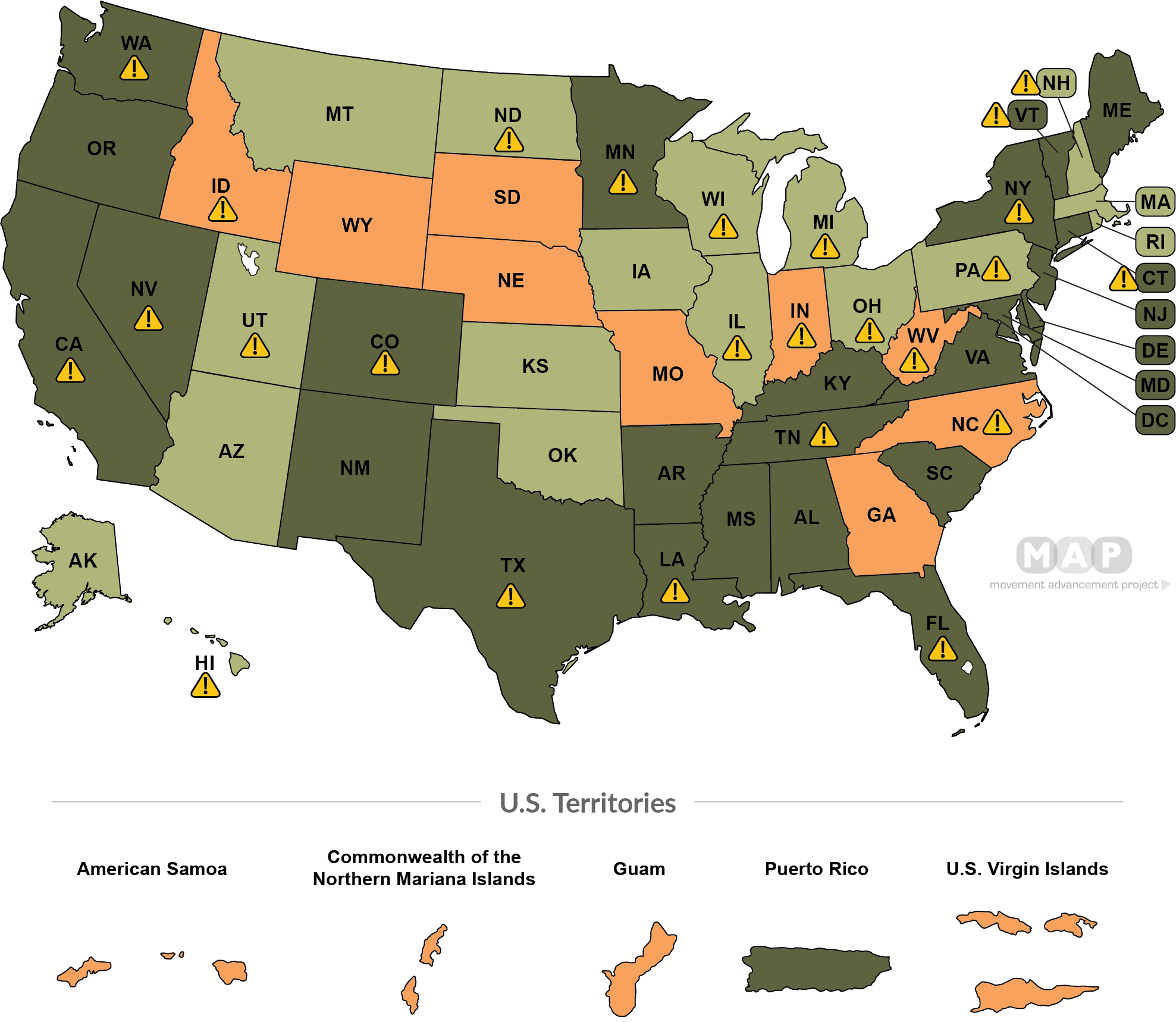
-
State law does not require publication of name change announcement (27 states , 1 territory + D.C.)
-
State law has unclear publication requirement, or requires publication but allows individual court discretion and/or broad option to waive requirement (14 states)
-
State law requires publication of name change announcement (9 states, 4 territories)
- State law includes additional restrictions and/or requirements for individuals with a criminal record (23 states)
Movement Advancement Project. "Equality Maps: Identity Document Laws and Policies." https://www.lgbtmap.org/equality-maps/identity_document_laws. Accessed 03/29/2025.
Percent of Transgender Population Covered by Laws
*Note: These percentages reflect estimates of the transgender population (ages 18+) living in the 50 states and the District of Columbia. Estimates of transgender people in the U.S. territories are not available, and so cannot be reflected here. Population estimates are from The Williams Institute.
- State has this lawPositive Law ,
- State does not have this lawNegative Law ,
 Gender Neutral 'X' Options Available
Gender Neutral 'X' Options Available
| State | Driver's License | Birth Certificate | Name Change |
| Citations | Citations | Citations | |
| Alabama | State does not have this law | State has this law | |
| Alaska | State has this law | ||
| American Samoa | State does not have this law | ||
| Arizona | |||
| Arkansas | State does not have this law | State has this law | |
| California |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Colorado |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Connecticut |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Delaware | State has this law | State has this law | |
| District of Columbia |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Florida | State does not have this law | State has this law | |
| Georgia | State does not have this law | State does not have this law | |
| Guam | State does not have this law | State does not have this law | |
| Hawaii |
State has this law |
||
| Idaho | State does not have this law | ||
| Illinois |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Indiana | State does not have this law | State does not have this law | |
| Iowa | State does not have this law | State does not have this law | |
| Kansas | State does not have this law | ||
| Kentucky | State does not have this law | State has this law | |
| Louisiana | State does not have this law | State has this law | |
| Maine |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Maryland |
State has this law |
State has this law | |
| Massachusetts |
State has this law |
 |
|
| Michigan |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Minnesota |
State has this law |
State has this law | |
| Mississippi | State has this law | ||
| Missouri | State does not have this law | State does not have this law | |
| Montana | State does not have this law | State does not have this law | |
| Nebraska | State does not have this law | ||
| Nevada |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| New Hampshire |
State has this law |
||
| New Jersey |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| New Mexico |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| New York |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| North Carolina | State has this law | State does not have this law | |
| North Dakota | State has this law | ||
| Northern Mariana Islands | State does not have this law | State does not have this law | |
| Ohio | State has this law | ||
| Oklahoma | State does not have this law | State does not have this law | |
| Oregon |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Pennsylvania |
State has this law |
||
| Puerto Rico | State has this law | State has this law | |
| Rhode Island |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| South Carolina | State does not have this law | State has this law | |
| South Dakota | State does not have this law | ||
| Tennessee | State does not have this law | State has this law | |
| Texas | State does not have this law | State has this law | |
| U.S. Virgin Islands | State does not have this law | ||
| Utah |
 |
 |
|
| Vermont |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| Virginia |
State has this law |
State has this law | |
| Washington |
State has this law |
 |
State has this law |
| West Virginia | State does not have this law | ||
| Wisconsin | |||
| Wyoming | State has this law | State does not have this law |


